Menu
Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
The following physics revision questions are provided in support of the physics tutorial on Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions. In addition to this tutorial, we also provide revision notes, a video tutorial, revision questions on this page (which allow you to check your understanding of the topic) and calculators which provide full, step by step calculations for each of the formula in the Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions tutorials. The Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions calculators are particularly useful for ensuring your step-by-step calculations are correct as well as ensuring your final result is accurate.
Not sure on some or part of the Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions questions? Review the tutorials and learning material for Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions
| Tutorial ID | Title | Tutorial | Video Tutorial | Revision Notes | Revision Questions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.6 | Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions |
Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions Revision Questions
1. An object moves from A (- 4m, 6m) to B (12m, 6m) to the reference point. Then, it moves from B (12m, 6m) to C (12m, 0m). The entire motion lasts for 10 s. What are the magnitudes of average speed (< v >) and average velocity (< v⃗ >) of the object?
- Average speed = 2.2 m/s; Average velocity = 17.1 m/s
- Average speed = 2.2 m/s; Average velocity = 1.7 m/s
- Average speed = 1.4 m/s; Average velocity = 1.0 m/s
- Average speed = 14 m/s; Average velocity = 10 m/s
Correct Answer: B
2. A car moves by 30 km due North for 30 minutes, then it moves by 80 km due East for 1 hour and finally it moves by 70 km due South for 1.5 hours. What are the magnitudes of average speed (< v >) and average velocity (< v⃗ >) of the car during the entire trip?
- Average speed = 60 km/h; Average velocity = 29.8 m/s
- Average speed = 180 km/h; Average velocity = 89.4 km/h
- Average speed = 60 km/h; Average velocity = 29.8 km/h
- Average speed = 180 m/s; Average velocity = 89.4 m/s
Correct Answer: C
3. An object moves from E to C and then from C to G as shown in the figure.
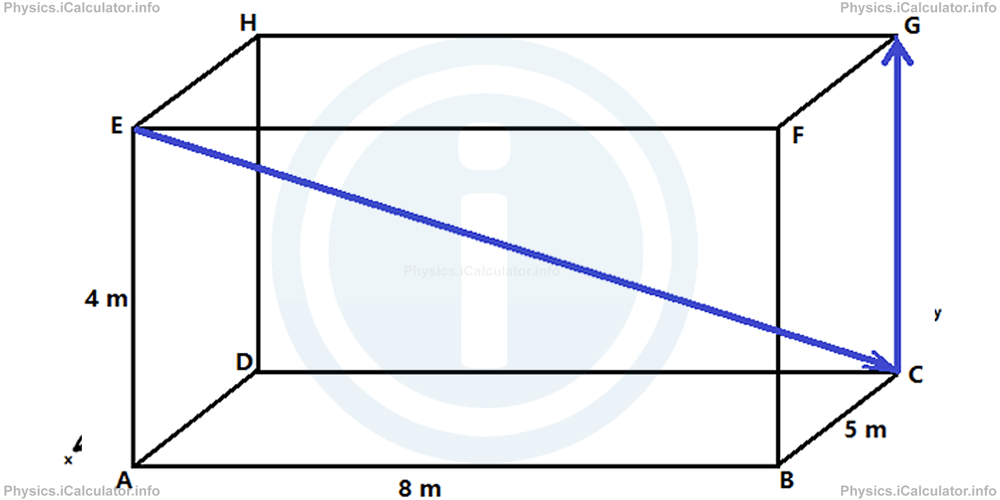
What are the magnitudes of average speed (< v >) and average velocity (< v⃗ >) of the object during the entire motion if the moving time from E to G is 5 s?
- Average speed = 2.8 m/s; Average velocity = 1.9 m/s
- Average speed = 3.4 m/s; Average velocity = 1.9 m/s
- Average speed = 2.7 m/s; Average velocity = 1.8 m/s
- Average speed = 3.4 m/s; Average velocity = 2.8 m/s
Correct Answer: A
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions" practice questions? People who liked the "Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions" practice questions found the following resources useful:
- Practice Questions Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this practice questions (see below)
- Kinematics Physics tutorial: Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions. Read the Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Kinematics
- Kinematics Revision Notes: Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions
- Check your calculations for Kinematics questions with our excellent Kinematics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Kinematics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning kinematics - read our next physics tutorial: The Meaning of Acceleration. Constant and Non-Constant Acceleration. Gravitational Acceleration
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics tutorial "Speed and Velocity in 2 and 3 Dimensions" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics tutorial (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.