Menu
Physics Lesson 16.1.6 - The Earth as a Giant Magnet. Two North Poles.
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on The Earth as a Giant Magnet. Two North Poles., this is the sixth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Introduction to Magnetism, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
The Earth as a Giant Magnet. Two North Poles.
We explained at the beginning of this tutorial that a bar magnet suspended in a thread points towards the two geographic poles. This is the reason why we use the terms North and South to describe the poles of a magnet. In addition, we explained that such a behaviour of bar magnets indicates the existence of Earth magnetic field, which determines the orientation of bar magnets in space.
Indeed, Earth is considered as a giant magnet containing its own magnetic field, whose lines as shown in the figure below.
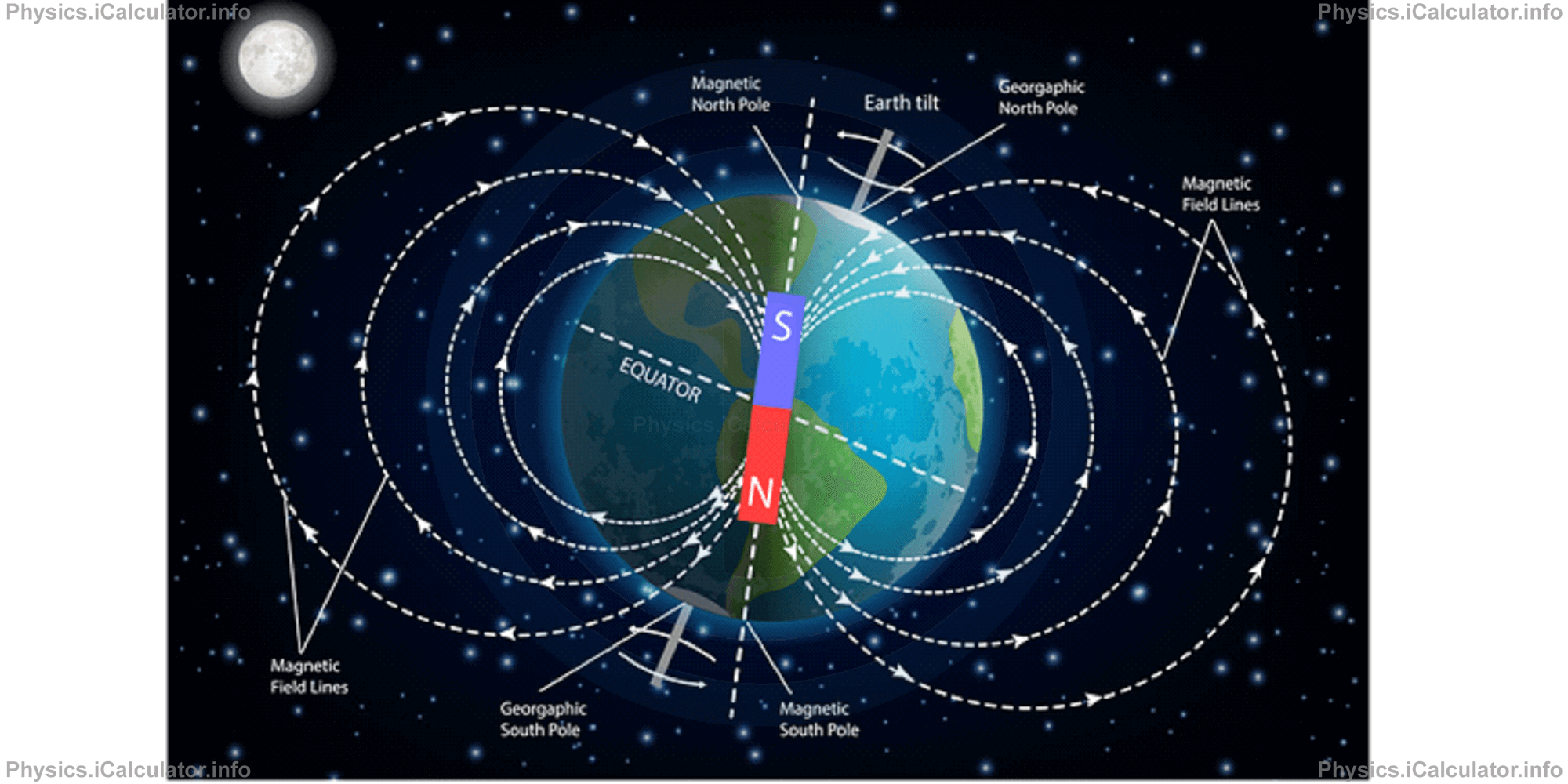
In fact, magnetic and geographic poles do not lie exactly in the same direction; they diverge from each other by an angle of about 220. This means when a traveller starts moving from equator in the direction of North Pole indicated by the magnet, he will not reach the geographic North Pole but he will instead end his motion about 2000 km away from it. In other words, if a person starts travelling from Africa towards the North Pole indicated by the suspended bar magnet, he will end his travel at north of Canada, not at the North Pole of the Earth. That's why there exist two distinct North Poles: one geographic and the other magnetic.
The device used from travellers to orient themselves - especially when sailing in oceans, during which it is very difficult to know the direction as no land is visible - is called compass. It consists on a small magnetic needle placed on a thin pin, parallel to a circular case in which the main directions are written.
The Earth's magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet extending from the North to the South magnetic pole. This means the magnetic field lines near the poles are vertical while in other positions they are parallel to the Earth surface, i.e. they are horizontal.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 16.1.6 The Earth as a Giant Magnet. Two North Poles.. There are 9 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Introduction to Magnetism, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Introduction to Magnetism Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "The Earth as a Giant Magnet. Two North Poles." physics lesson? People who liked the "Introduction to Magnetism lesson found the following resources useful:
- Magnetic Earth Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this magnetic earth (see below)
- Magnetism Physics tutorial: Introduction to Magnetism. Read the Introduction to Magnetism physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Magnetism
- Magnetism Revision Notes: Introduction to Magnetism. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Introduction to Magnetism
- Magnetism Practice Questions: Introduction to Magnetism. Test and improve your knowledge of Introduction to Magnetism with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Magnetism questions with our excellent Magnetism calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning magnetism - read our next physics tutorial: Magnetic Field Produced by Electric Currents
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Introduction to Magnetism" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™
- Angular Frequency Of Oscillations In Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Calculating Magnetic Field Using The Amperes Law
- Capacitive Reactance Calculator
- Current In A Rl Circuit Calculator
- Displacement Current Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In The Capacitor Of A Rlc Circuit In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Electric Power In A Ac Circuit Calculator
- Energy Decay As A Function Of Time In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Energy Density Of Magnetic Field Calculator
- Energy In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Faradays Law Calculator
- Frequency Of Oscillations In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Impedance Calculator
- Induced Emf As A Motional Emf Calculator
- Inductive Reactance Calculator
- Lorentz Force Calculator
- Magnetic Dipole Moment Calculator
- Magnetic Field At Centre Of A Current Carrying Loop Calculator
- Magnetic Field In Terms Of Electric Field Change Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Long Stretched Current Carrying Wire Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Toroid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Produced Around A Long Current Carrying Wire
- Magnetic Flux Calculator
- Magnetic Force Acting On A Moving Charge Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Magnetic Force Between Two Parallel Current Carrying Wires Calculator
- Magnetic Potential Energy Stored In An Inductor Calculator
- Output Current In A Transformer Calculator
- Phase Constant In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Factor In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Induced On A Metal Bar Moving Inside A Magnetic Field Due To An Applied Force Calculator
- Radius Of Trajectory And Period Of A Charge Moving Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Self Induced Emf Calculator
- Self Inductance Calculator
- Torque Produced By A Rectangular Coil Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Work Done On A Magnetic Dipole Calculator